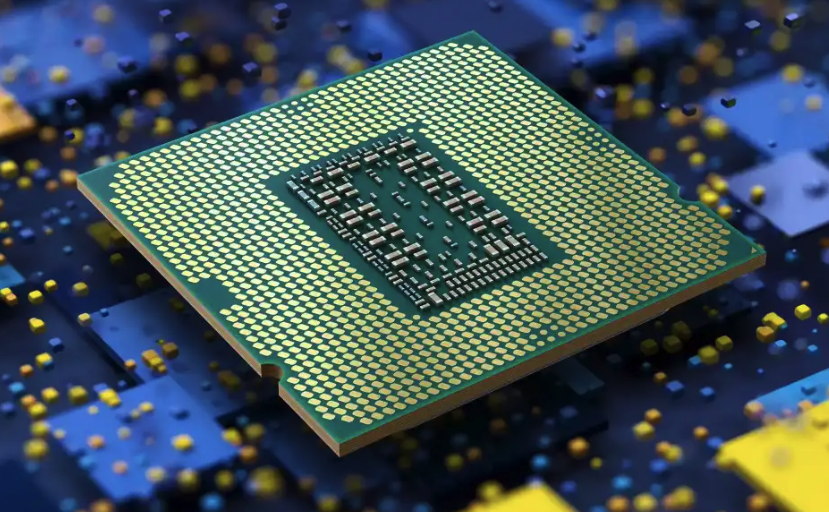
CPU is one of the most complex parts of computers. No one can think of a computer without a CPU. It has various sub-parts that help it to complete the processing of various commands at the same time. It has many registers to store the temporary file. The part of the CPU works like RAM and cache memory, but its storage capacity is much lesser in comparison to them. CPU registers that have numerical information are fast to access. In the article, we will discuss where does the CPU store its computation and also get to know about different registers.
The central processing unit or CPU works as a brain for a computer. It processes the data and releases the output. We can also say that the CPU is the main point where all the calculations are conducted and stored. Here we will find out where the CPU stores its computations.
CPU manages the input, output and process data entered through input devices. It’s a great tool to calculate big numbers in nanoseconds. If you are techno-savvy, then you must want to know how this part of the computer computes data and where does the CPU store its computations.
Where Does the CPU Store Its Computations?
The work of the central processing unit gets clear with the name of this component of computers. It’s the place where all processing work is completed. The fast computation speed of computers is amazing. All these computations are stored in the CPU’s registers. Before you think of some imaginary register similar to the one you use in class, let us clarify that these registers are similar to RAM. They are like some temporary files which get vanish after a certain period. The registers are smaller but faster than any temp file on the hard disk.
CPU has different registers to perform different tasks; for example, to store the addresses, it has the address register; to store numerical information, it has a data register. In the same way, for a different purpose, there is a different register in the CPU. So the one word answer to your query; where does the CPU store its computations is registers. The tiny register takes less time in the execution of information. Generally, users think that cache memory and RAM are where the CPU has its computation but registers come before the computation goes to the cache memory.
Similarly, most computer users cannot differentiate between registers and cache memory. But they both are different in terms of functionality and speed. As mentioned earlier, registers are faster than the cache, and the data stored in the registers can be used twice or thrice in one cock cycle, but the life of files in cache memory or RAM is comparatively short. Now you know that the CPU uses both the registers and cache memory to store its computation, but initially, it goes to register. So, let’s check out the difference between the register and the cache memory and get some information on the part played by cache memory in storing the computation.
How Register and Cache are different?
So CPU needs both the register and cache to store computation, but why does it need two of its components for the same task? Register and cache have a few similarities, but they are different. For example, the command execution process is different, so is their response time.
Above the article, we have described how the register stores the data. Now let’s know more about the CPU cache. The cache is an unstable memory that stores the data in the CPU, so data vanishes soon. Like registers, a different cache is used for a different task. We can divide the CPU cache into the following three categories;
- Instruction Cache
- Data Cache and
- Translation lookaside buffer
Names assigned to different types of cache resemble their work. The data cache has three more levels; L1, L2, and L3. The names assigned to each level are based on their size and speed. The L1 level of the data cache is the fastest but smallest, and the L3 is the biggest one with the slowest speed. CPU cache memory is a temporary one, and it has the data that the CPU might need again. Cache memory is very fast, but registers are faster than this. Generally, people refer to cache as the fastest but most volatile memory. CPU register beats them with their speed. To understand the difference in the speed of register and cache, you can assume register as Data cache level 0.
The L1 data cache is the fastest with the smallest size, and registers are much smaller and faster than this. Registers have such a small memory that they can only have a few calculations with partial results. A register may have a medium part of the computation, and another can have the last one. A register keeps the calculation until the last result comes out. It’s the quickest part of the CPU to store computation. Registers and cache both play a crucial role in storing the CPU’s computation. Without one of them, the CPU’s performance will be affected, and it will become extremely slow. Register stores the CPU computation, but cache also plays a crucial role. The cache memory keeps the data for further processing. Without cache, the CPU has to fetch the data from RAM, which will be time-consuming for the CPU.
Conclusion
So, now you know the answer of where does the CPU store its computation; it’s not cache but CPU register. The CPU stores data in the register for maximum efficiency as registers are the fastest. You can also mention that cache also plays an important part in storing the CPU’s computation. For a faster CPU, both register and cache are essential.